astronomy
Latest

The Hayden Planetarium’s new show celebrates unmanned space probes
The astronomy I learned as a kid was pretty limited — the Earth revolves around the Sun and, of course, the whole "My Very Energetic Mother Just Served Us Nine Pizzas" thing. Of course, that expression no longer applies because our understanding of the solar system is a lot more nuanced these days. Not just because we're adults now, but because the entire field has been revolutionized by probes, plumbing the depths of distant bodies and returning that data to us over decades. That deeper understanding of our solar system is at the heart of the American Museum of Natural History's new space show, Worlds Beyond Earth, but its unsung hero is the technology that made it possible.

Discovery shows early galaxies could have very short lives
You'd think that galaxies from the young universe would still be thriving, but that's not necessarily the case. Researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute and the National Observatory of Japan have discovered the farthest known dying galaxy (that is, with greatly suppressed star formation) known to date at about 12 billion light-years away. In other words, it was already waning roughly 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang -- the first galaxies had come into being about a billion years earlier. The team used a combination of Keck telescope systems and the Very Large Telescope to measure the motion of stars and learn that the galaxy's core was nearly fully formed.

NASA's closest-ever Sun flybys reveal how solar wind works
As promised, NASA has presented the first results from the Parker Solar Probe -- and they're already providing a treasure trove of insights regarding the Sun. Most notably, the solar wind doesn't behave entirely like scientists expected. There are flips in the Sun's magnetic field direction (nicknamed "switchbacks") that manifest in the solar wind inside Mercury's orbit, but not further. Moreover, the sideways movement of the solar wind near the Sun was not only "much stronger" than expected, but straightened out sooner than predicted as well.

Astronomers find stellar black hole so large it shouldn't exist
Just because there's a picture of a black hole doesn't mean astronomers have figured out how they work. Chinese-led researchers have detected a stellar black hole in the Milky Way with a mass so large that it breaks current stellar evolution models. LB-1, a black hole 15,000 light-years away, has a mass 70 times greater than that of the Sun -- previous estimates suggested that no stellar black hole would have more than 20 times the Sun's mass. Scientists expected many dying stars to shed most of their gas, making something this large impossible without readjusting theories.
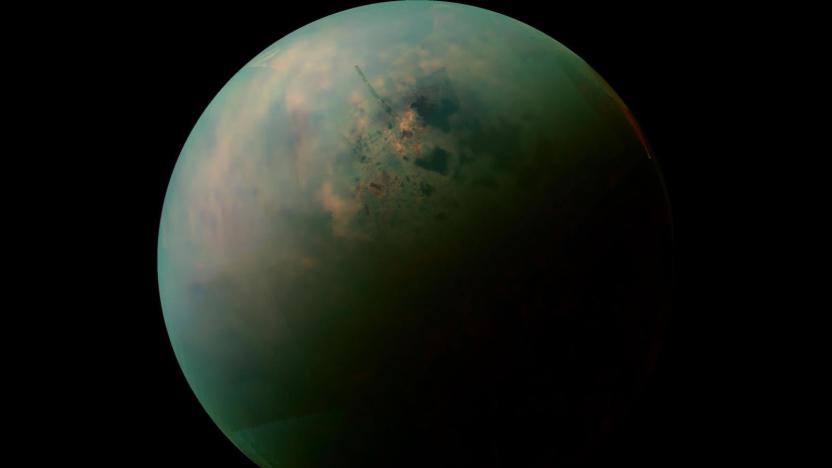

Astronomers create first global map of Saturn's moon Titan
Scientists finally have a comprehensive view of Titan, Saturn's largest moon. A team of astronomers has created the first global map of Titan by using the Cassini probe's over 100 fly-bys to stitch together both imagery and radar measurements. The comprehensive view reveals a landscape that's almost as diverse as Earth in key way.

NASA renames Kuiper Belt object following controversy
NASA's nickname for the distant Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU69, Ultima Thule, has been more than a little contentious. While it has innocuous meanings, Ultima Thule is also the term white supremacists use to refer to a mythical homeland. The agency is sidestepping that controversy, however. It just officially named the object Arrokoth, or "sky" in the Powhatan/Algonquian language. NASA received the consent of the Powhatan tribe before making the change.

Scientists discover water vapor on an exoplanet with a rocky core
Water vapor is common in gas giants; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune all have H2O floating around in their atmospheres. But water on a rocky planet is exceedingly rare, making the discovery of water vapor -- and possibly even rain -- on the exoplanet K2-18 b a surprising breakthrough.

NASA selects proposals for smallsats built to study deep space
NASA is expanding plans to use small satellites (aka smallsats) to explore the Solar System. The agency has picked two proposals for smallsat technology that would improve observations in deep space, where they could help improve models that predict space weather. One, Science-Enabling Technologies for Heliophysics (SETH), would demo both optical communications as well as a detector that can spot fast-moving chargeless atoms emanating from the Sun. Solar Cruiser, meanwhile, would include both a giant 18,000 square foot solar sail as well as a coronagraph that could study both the Sun's magnetic field as well as the velocity of coronal mass ejections.

Supercomputer creates millions of virtual universes
How do you understand the development of galaxies when even the younger examples are frequently billions of years old? Simulate as many universes as you can, apparently. Researchers at the University of Arizona have used the school's Ocelote supercomputer as a "UniverseMachine" that generates millions of mini universes to see how well they line up with the real cosmos. Rather than try to portray every nuance of the whole universe (even a single fully modeled galaxy would require far too much computing power), the team devised a system that had just enough resolution to scale from supernovae to a "sizeable chunk" of observed space. Each virtual universe had a different set of rules, and it was largely a matter of seeing which simulations lined up the closest with real data.

Scientists find the largest observed black hole to date
Astronomers aren't done with major black hole discoveries this year. The Max Planck Institute's Kianusch Mehrgan and colleagues have found the largest black hole ever observed at the center of Holm 15A, a galaxy about 700 million light-years away. It's more than twice as large as the previous observed record-setter at 40 billion times the mass of the Sun, and 10,000 times the mass of the black hole at the core of the Milky Way.
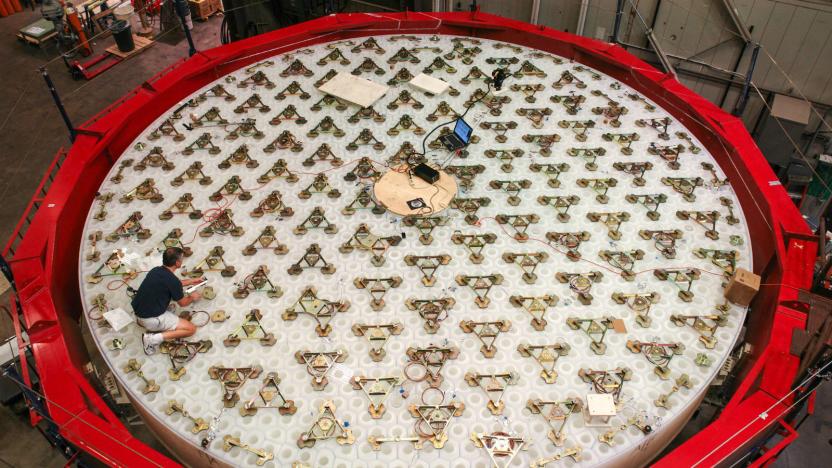

The world’s largest telescope is one step closer to completion
The world's largest telescope is one step closer to completion. This month, the team working on the Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) completed the second of seven primary mirror segments, a process that began in January 2012.
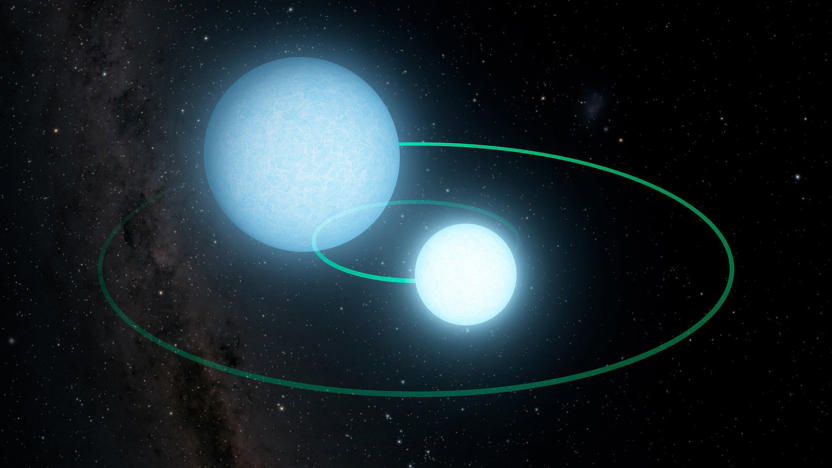
Two dead, dancing stars challenge astronomers' expectations
Stars still have plenty of surprises despite (or perhaps, because of) advances in astronomy. Researchers using Caltech's Zwicky Transient Facility have discovered a binary white dwarf system 8,000 light-years away, ZTF J1539+5027, where the two dead stars orbit each other every seven minutes. That's the second-fastest pair of white dwarfs seen to date, and the fastest such "eclipsing" system (where one passes between its partner and Earth). This isn't the first time they've seen one white dwarf 'eat' the other, but it's rare to catch this cannibalization in the act.

Astronomers believe the young Milky Way once swallowed a dwarf galaxy
Astronomers believe they've mapped an important sequence of events that shaped our galaxy 10 billion years ago. In a paper published in Nature Astronomy today, researchers from the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias (IAC) share their findings that a dwarf galaxy, Gaia-Enceladus, once collided and merged with the early Milky Way. Their discovery offers a new understanding of how the Milky Way formed.
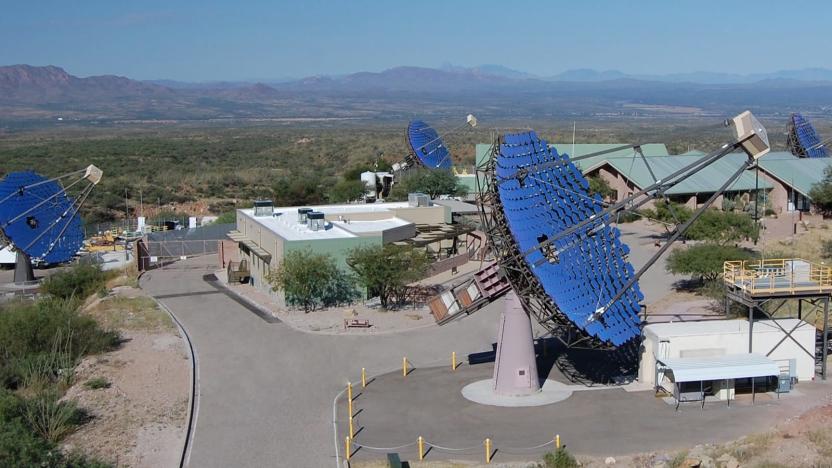

Breakthrough searches for signs of alien life in ultra-fast light pulses
Internet investor Yuri Milner's search for extraterrestrial life now includes a hunt for, effectively, interstellar Morse code. Breakthrough Listen is teaming with the partners behind VERITAS (the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) to search for nanoseconds-long optical pulses that could indicate the presence of aliens trying to flash messages across the cosmos. The collaboration will use all four telescopes at once to check for these light-based "beacons," which would could be brighter than stars observed in the same direction.

Russia launches X-ray telescope to find 'millions' of black holes
Russia is back in the business of space observation after losing control of a radio telescope a the start of 2019. The country has successfully launched Spektr-RG, an X-ray telescope co-developed with Germany's help. The vessel will take 100 days to reach its final destination of Lagrange Point 2, where it can conduct studies in stable conditions a million miles from Earth. When it gets there, though, it could significantly reshape human understanding of the universe.
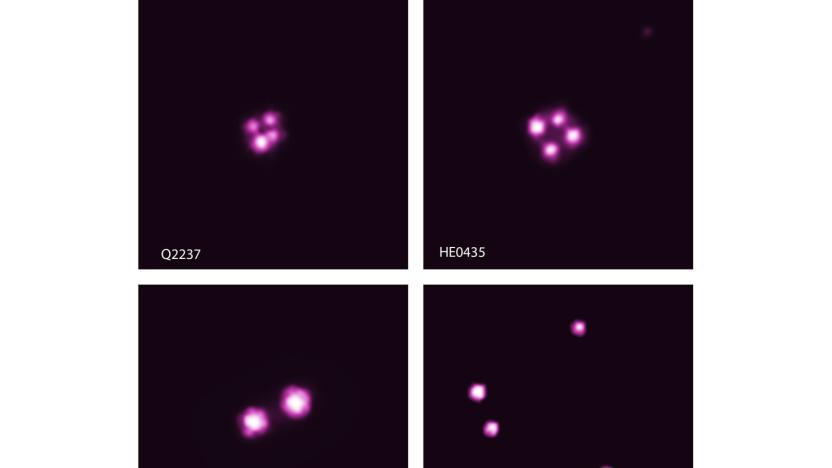
X-rays help astronomers detect spinning black holes
It can be tricky to measure the spin of a black hole, particularly when it's hard to see them, but astronomers have pulled off just such a feat. They've gauged the spins of five supermassive black holes through a combination of data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and gravitational lensing, or the use of gravity from celestial bodies to magnify very distant objects.

NASA's TESS spacecraft discovers its smallest exoplanet to date
NASA's TESS spacecraft is continuing to find ever-smaller planets -- and that now includes planets smaller than the human homeworld. The vessel has found a planet in the L 98-59 system, L 98-59b, that's 80 percent the size of Earth -- and 10 percent smaller than TESS' previous tiniest finding. You won't be planning a vacation any time soon, unfortunately. The system is 34.6 light-years away, and all of the planets discovered so far (there are larger 59c and 59d planets) sit in the "Venus zone" where a runaway greenhouse gas effect could render them uninhabitable.
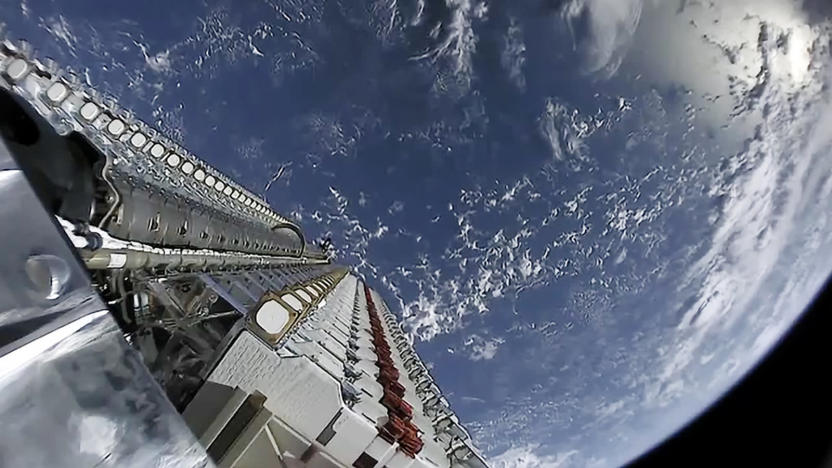

SpaceX's internet satellites could be a problem for astronomers
As helpful as SpaceX's Starlink satellites may be, they could be a pain for astronomers. The Harvard-Smithsonian Center's Jonathan McDowell and others have observed that the internet satellites are bright enough to cause a "problem" for astronomy, and the eventual constellation of roughly 12,000 satellites could complicate humanity's view of the night sky. It would triple the number of satellites in orbit, CNET noted, forcing telescope operators to account for the objects.

This is the first real picture of a black hole
Yes, it happened. After years of relying on computer-generated imagery, scientists using the Event Horizon Telescope have captured the first real image of a black hole. The snapshot of the supermassive black hole in the Messier 87 galaxy (about 55 million light years away) shows the "shadow" created as the event horizon bends and sucks in light. It also confirms that the black hole is truly huge, with a mass 6.5 billion times that of the Sun. As you might imagine, taking this picture was tricky -- it required worldwide collaboration that wasn't possible until recently.

Watch the first ever image of a black hole be livestreamed here
What does a black hole look like? Black, probably. And big. That sounds pretty vague, but as the gravitational forces of a black hole are so strong even light is overpowered by them, we've never had a comprehensive image of one before. Until now. Today, scientists from six cities around the world will unveil the first ever image of a black hole -- called Sagittarius A* -- and you can watch the historic announcement live online. (Update: the image has been released. Check it out here!)




