DNA
Latest
23andMe hack now estimated to affect over half of customers
A hack that affected 23andMe back in October is estimated to have exposed significantly more profiles than previously reported.
Malak Saleh12.05.2023
23andMe user data breached in credential-stuffing attack
23andMe user data is circulating on hacker forums. The company confirmed the leak occurred through a credential-stuffing attack, according to BleepingComputer.
Malak Saleh10.07.2023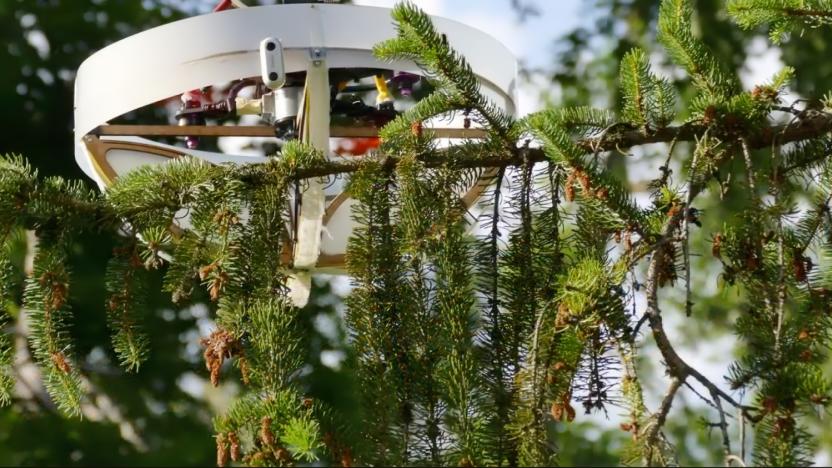
Researchers created a sticky drone to collect environmental DNA from forest canopies
Swiss researchers trialed a method that uses a drone with an attached cage to collect environmental DNA from high treetops.
Will Shanklin01.27.2023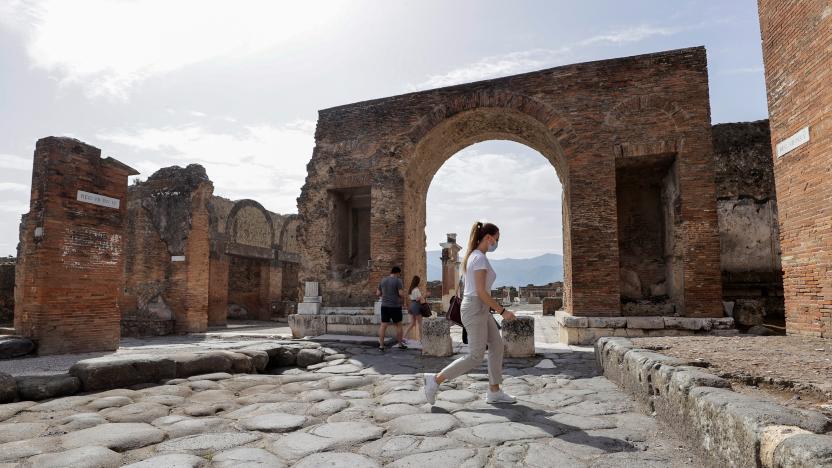
Researchers sequenced the genome of one of Pompeii’s ancient inhabitants
Thanks to the latest advances in DNA sequencing technology, we now know more about one of Pompeii's residents.
Igor Bonifacic05.29.2022
Massive DNA study of human cancers offers new clues about their causes
UK scientists analyzed the complete genetic makeup of 12,000 tumors from NHS patients.
Mariella Moon04.22.2022
Las Vegas police solve an old murder case using record-low volume of DNA
Las Vegas police have solved a cold murder case using a record-low volume of DNA to conduct gene sequencing.
Jon Fingas07.25.2021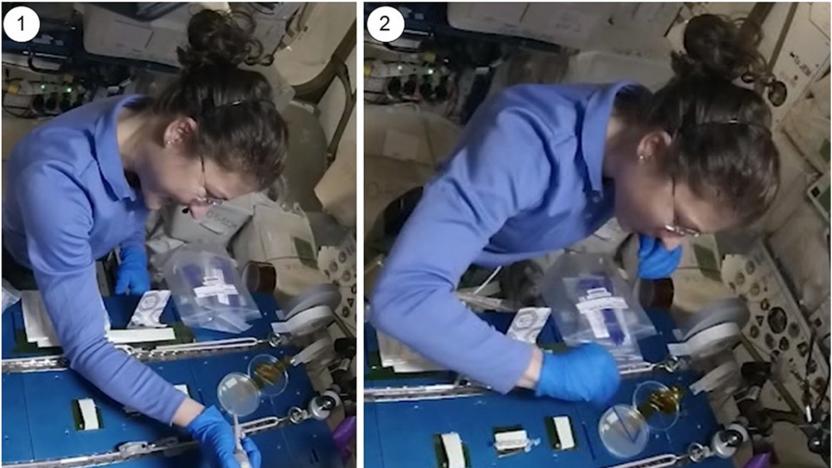
Astronauts show how CRISPR gene editing works in space
Astronauts have successfully used CRISPR gene editing in space for the first time, paving the way for studies of how space travel affects the human body.
Jon Fingas07.04.2021
Scientists show you can collect DNA from the air
Scientists have shown that you can collect DNA from the air, opening new ways to study airborne diseases and investigate crimes.
Jon Fingas04.04.2021
NVIDIA and Harvard researchers use AI to make genome analysis faster and cheaper
NVIDIA and Harvard scientists have developed an AI that is able to run single-cell experiments and analyze the genome faster and cheaper than traditional methods.
Nicole Lee03.08.2021
Scientists sequence 64 human genomes to better reflect genetic diversity
Scientists have sequenced 64 full human genomes to better understand genetic diversity in the species.
Jon Fingas02.28.2021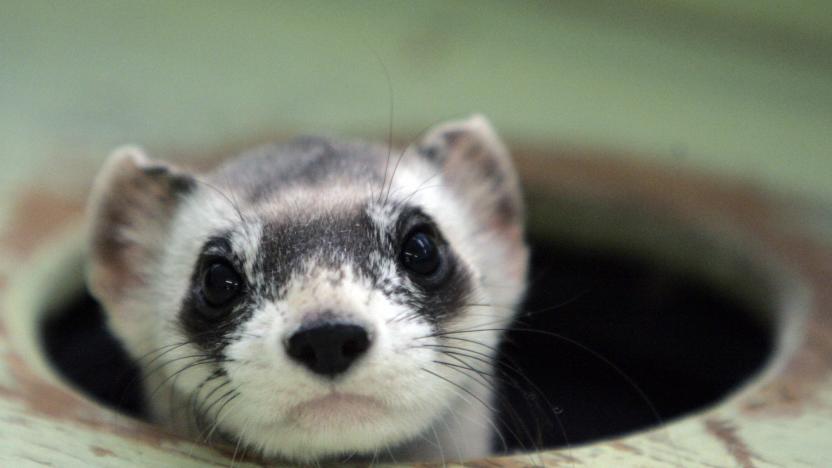
A ferret is the first North American endangered animal to be cloned
Scientists have cloned the first North American endangered species, successfully producing a black-footed ferret.
Jon Fingas02.20.2021
23andMe is going public as it pushes further into healthcare
23andMe is becoming a publicly-traded company through a merger with VG Acquisition, taking the DNA testing firm further into healthcare and research.
Jon Fingas02.04.2021
Hitting the Books: Widespread DNA testing could intensify American racism
Every time we log on, our personal data including where we go, what we search for, who we interact with and what we buy is scraped, siphoned, collected, analyzed, categorized and monetized in the everlasting effort to design and distribute more effective, more personalized advertising. In her latest book, Cyber Privacy: Who Has Your Data and Why You Should Care cybersecurity expert April Falcon Doss examines what sorts of data are being collected, how they’re being used (to both our benefit and detriment) and what can be done to keep your digital life history from being leaked across the internet. In the excerpt below, Doss takes a terrifying look at how our infatuation with Ancestry.com and other genealogical testing services has metastasized into a means for the Border Patrol and ICE to further harass and discriminate against black and brown people in America.
Andrew Tarantola10.24.2020
CRISPR gene editing pioneers win the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
CRISPR gene editing pioneers Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna have won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for a 'revolutionary' impact on science.
Jon Fingas10.07.2020
Scientists rename genes because Microsoft Excel reads them as dates
Scientists have been renaming human genes to prevent Microsoft Excel from misreading them as dates and corrupting data.
Jon Fingas08.06.2020
A security breach opened up access to a genealogy site’s DNA profiles
A security breach changed the permission settings on millions of profiles in GEDmatch, a DNA database used by genealogists.
Christine Fisher07.23.2020
'Resurrected' mammoth DNA helps explain why the species went extinct
Reviving the woolly mammoth is still a tall order. However, technology might be far enough along to help explain why the elephant precursor went extinct in the first place. Scientists have 'resurrected' genes from a population of mammoths that survived on a Siberian island until around 4,000 years ago to see what might have contributed to this relic herd dying out. After resurrecting a mammoth's genes through cells in culture, they compared it against both other mammoths and Asian elephants to look for problematic mutations based on known genetic behavior.
Jon Fingas02.08.2020
23andMe lays off 100 workers amid shrinking demand for DNA tests
If you're skittish about DNA testing services, you're not the only one -- and it's directly affecting one of the heavyweights in the field. The 23andMe team is laying off about 100 workers, or 14 percent of its total workforce, in light of declining sales. The job cuts will focus on units responsible for growing and scaling the company. In the months ahead, 23andMe expects to cut back its work on clinical studies and focus more on its home testing and therapeutic offerings.
Jon Fingas01.23.2020
The best DNA testing kit
By Amadou Diallo This post was done in partnership with Wirecutter. When readers choose to buy Wirecutter's independently chosen editorial picks, Wirecutter and Engadget may earn affiliate commission. Read the full guide to DNA testing kits. Consumer-oriented DNA testing services come with inherent privacy risks and are bound by few legal guidelines regulating the use of your data. The ramifications of sharing your DNA with for-profit companies are continuously evolving. Opting into a recreational DNA test today will likely have future consequences that no one has even considered yet. If you're comfortable with that, we think AncestryDNA is the most effective service for people who want to learn more about their ethnic roots or find contemporary relatives. We've come to this conclusion after more than 80 hours of research and two-plus years of reporting that included evaluating the results from a test panel representing every major population group. The aptly named AncestryDNA test stood out as the best ancestry DNA test because it presented the test results in a clearer manner than other services and placed the information in a useful historical context. Since all the DNA services we tested provided broadly similar results for the ethnic origins of our panel of testers, AncestryDNA's better reports and interface gave it a clear advantage. Plus, for people seeking distant cousins or even biological parents, the company's claimed DNA database of 10 million customers—twice the size of its closest competitors—increases the odds of successful matches. Unlike the other services we tested, however, AncestryDNA cannot track your maternal and paternal heritage independently or trace your ancient migration path out of Africa. 23andMe offers the same type of ethnicity estimates (and privacy risks) as AncestryDNA at a similar price. With a DNA database of 5 million users, it may offer smaller odds of connecting with unknown relatives, but it does have the most polished site design, which makes navigating the myriad charts, reports, and explanatory documents easier than on competitors' sites. For male testers, 23andMe can provide a look at the ancient migration paths of both maternal and paternal lines independently. And while we don't cover biomedical testing in this guide, 23andMe does offer its customers a suite of reports on potential health indicators as a paid add-on service. FamilyTreeDNA offered broadly similar ethnicity estimates for our testing panel as AncestryDNA and 23andMe. Those concerned about privacy should know that it is the only service we're aware of that is voluntarily providing customer data access to law enforcement. FamilyTreeDNA does, however, provide the most comprehensive suite of testing options, offered as add-ons to the basic ethnicity test, than any service we evaluated. These additional tools should satisfy nearly any genealogy buff looking to explore their connections to early human migration or find relatives from one particular side of their family tree. The company's à la carte approach can quickly add up though. You can easily spend more than three times the testing cost of AncestryDNA or 23andMe.
Wirecutter12.13.2019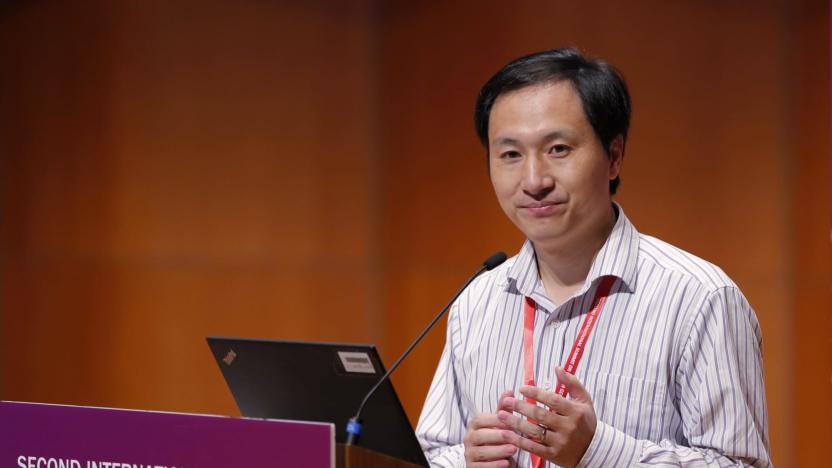
Recommended Reading: A year later, the CRISPR babies are still a mystery
Why the paper on the CRISPR babies stayed secret for so long Antonio Regalado, MIT Technology Review A year has passed since Chinese biophysicist He Jiankui presented work on editing the DNA of two girls while they were still embryos. Ethical issues with his actions abound, and even after all this time, there's still missing details on exactly what did/didn't happen. MIT Technology Review has several pieces on the story this week. Those include unpublished portions of the research manuscript and an explanation of why it hasn't been published by either of the two influential scientific journals He sent it to.
Billy Steele12.07.2019